© 2025 MJH Life Sciences™ , Patient Care Online – Primary Care News and Clinical Resources. All rights reserved.
Lipid Guidelines, Compared: ACC/AHA and ESC/EAS
The European and American guidelines on dyslipidemia management overlap but also diverge in critical ways. A Johns Hopkins cardiologist highlights similarities and differences.
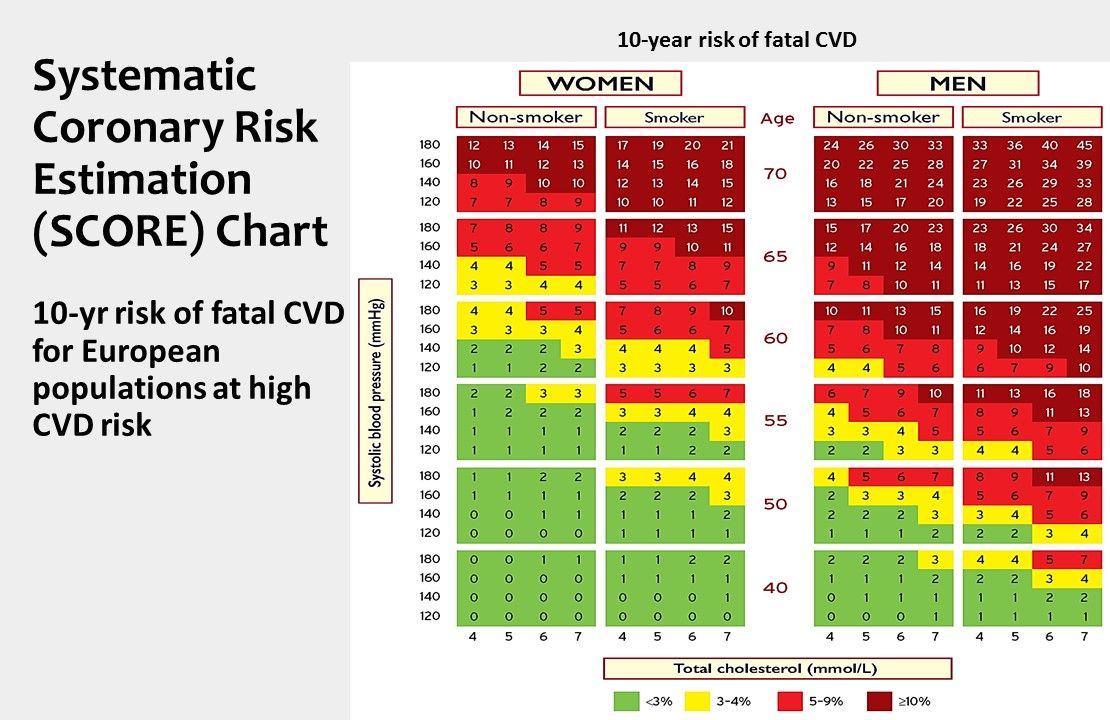
ESC/EAS Systematic Coronary Risk Estimation (SCORE) Chart. The Europeans use 2 charts, one for low and one for high risk regions of Europe. Both rely on systolic BP, sex, smoking status, and total cholesterol, whereas the US risk calculator also includes diabetes status, diastolic BP, statin and ASA use, race, and HDL and LDL levels. Additionally, the SCORE chart cannot be used in those with overt CVD, DM, CKD, or familial HLD since these patients are at high risk to begin with.
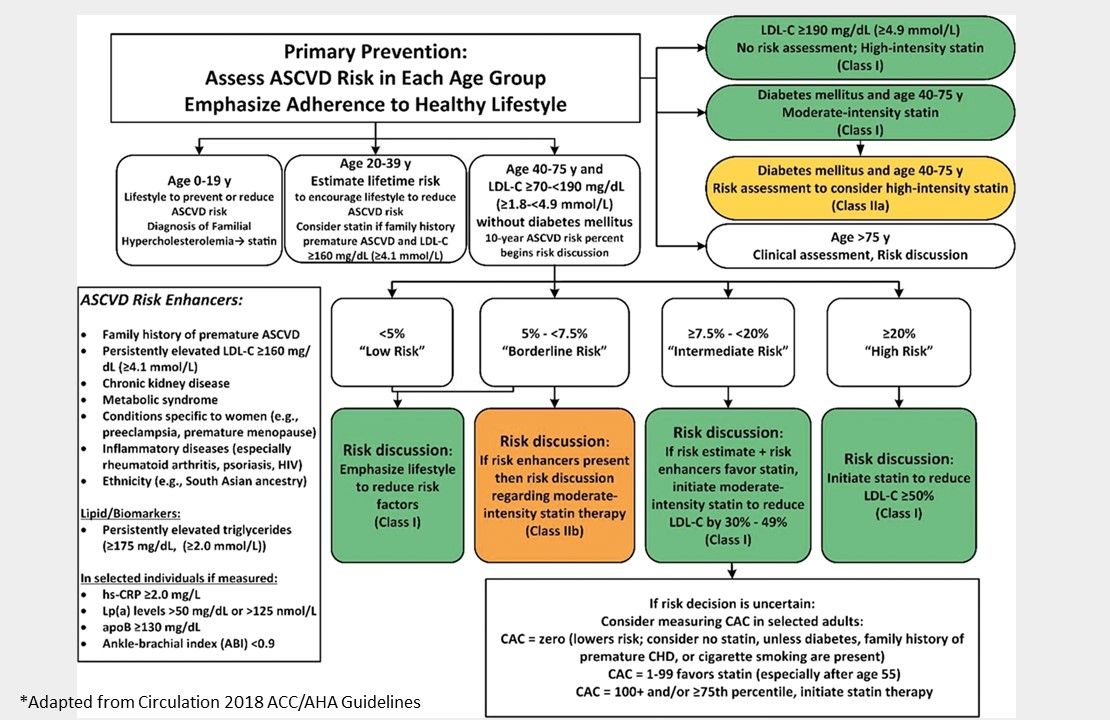
This chart from ACC/AHA is helpful to determine level of risk for primary prevention. In those aged 40-75 yrs, use the risk calculator to determine the level of risk (ie,low, borderline, intermediate, or high). Then, use the chart to guide initiation of statin therapy and targets for LDL-C reduction. The chart also includes how to approach statin therapy in certain populations (DM, LDL-C >190 mg/dL) and lists certain ASCVD risk enhancers that may help clarify the patient's level of risk.
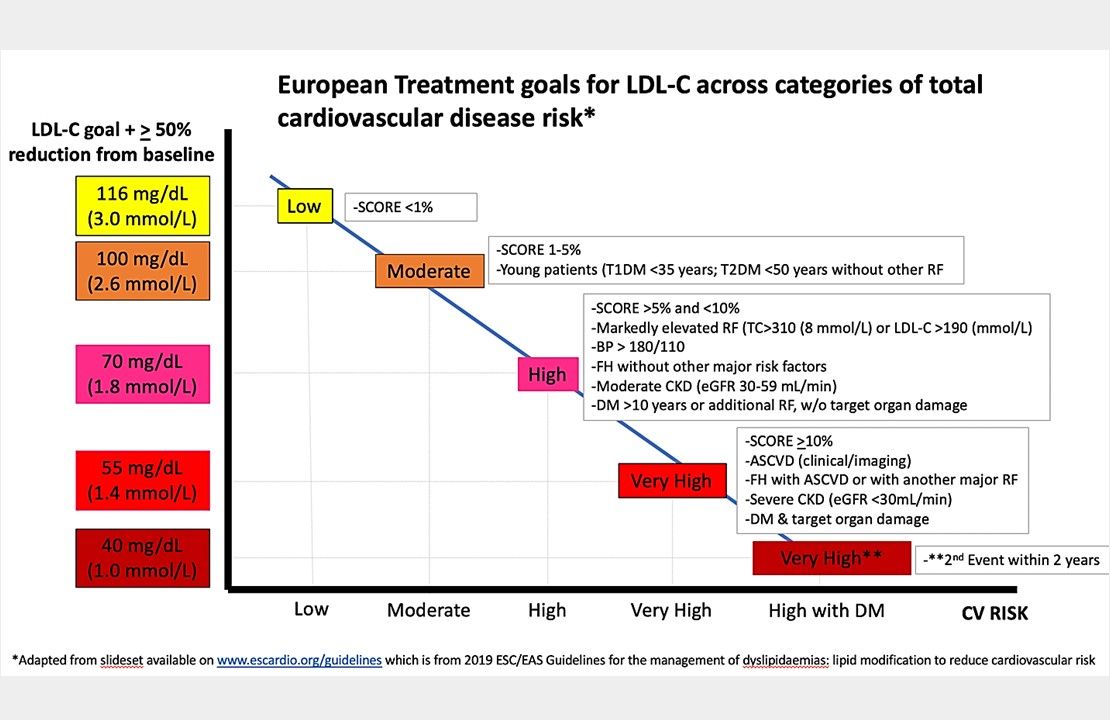
European treatment goals for LDL-c across categories of total CVD risk. After determining level of risk based on either the SCORE chart or other factors (presence of CKD, DM, FH, etc) listed in the outlined boxes along the X-axis, look at Y-axis to determine the target LDL-C, based on the level of risk. From 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for management of dyslipidaemias.
Once you determine the level of risk based on either the SCORE chart or other factors (presence of CKD, DM, FH, etc.) listed in the outlined boxes along the X-axis, you then look at the Y-axis to determine the target LDL-C based on the level of risk.
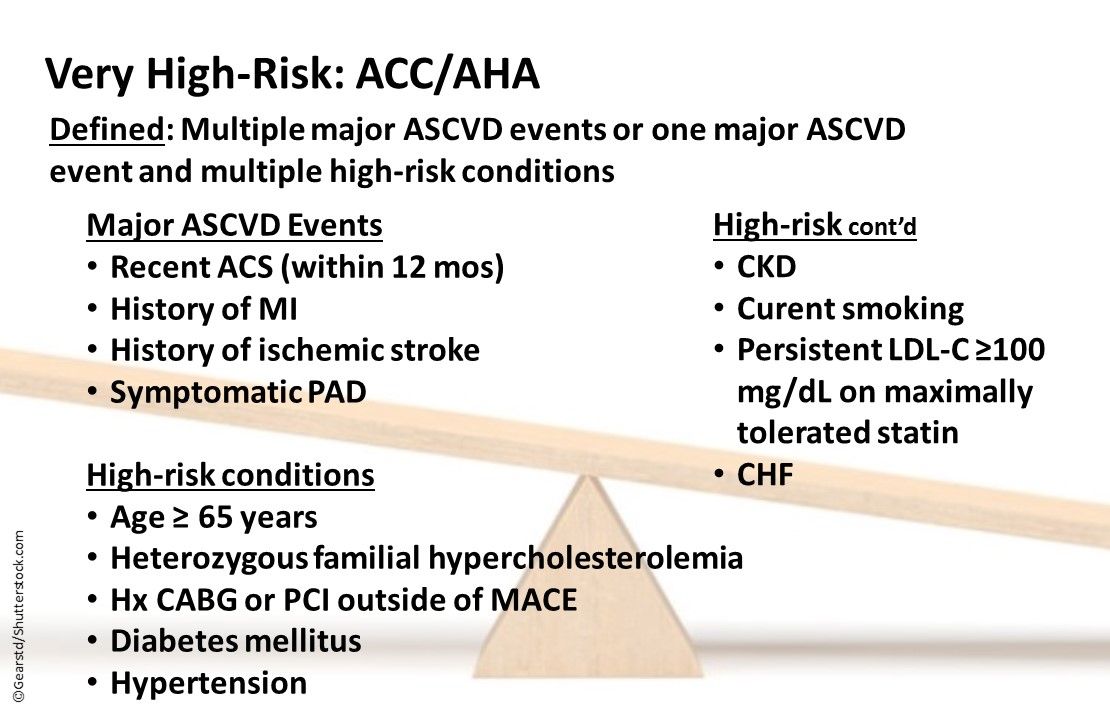
ACC/AHA Very High-risk Patients: Multiple major ASCVD events or one major ASCVD event and multiple high-risk conditions
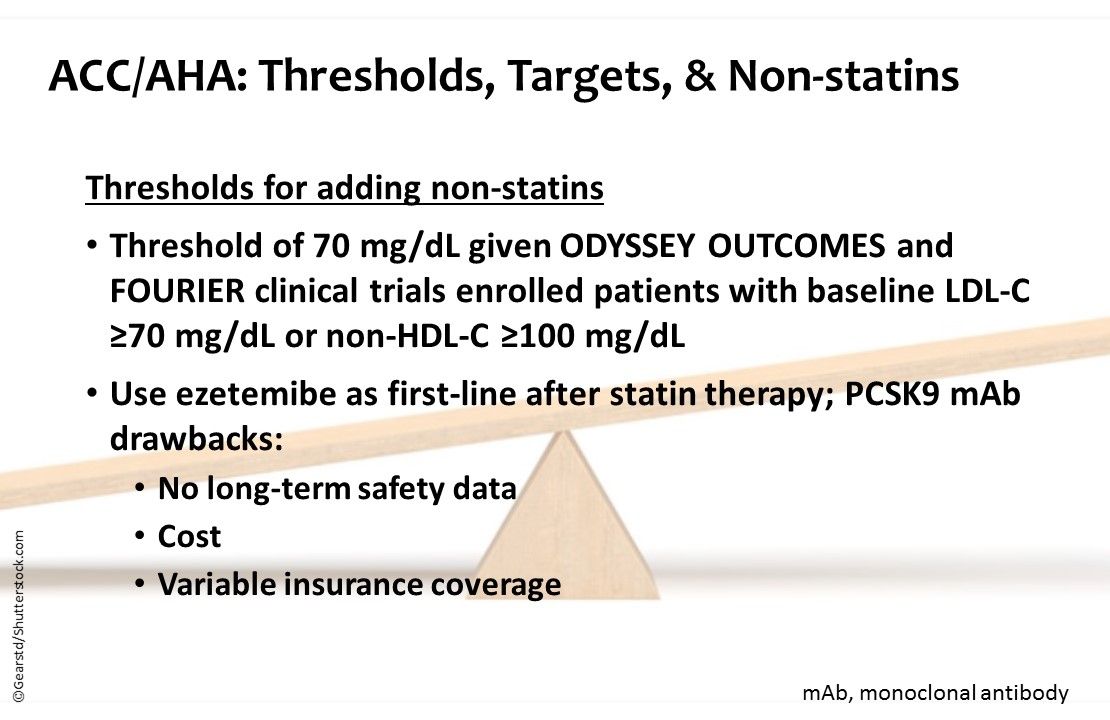
ACC/AHA: Thresholds, Targets, & Non-statins. Threshold of 70 mg/dL given ODYSSEY OUTCOMES and FOURIER clinical trials enrolled patients with baseline LDL-C ≥70 mg/dL or non-HDL-C ≥100 mg/dL

ESC/EAS: Thresholds, Targets, & Non-statins. ESC/EAS cite FOURIER & ODYSSEY OUTCOMES to support a IIb recommendation for a goal of <40 mg/dL (<1.0 mmol/L) in patients who experience a second vascular event within 2 years, while taking maximally tolerated statin therapy.

Summary: ACC & ESC Lipid Guidelines Similarities/Differences
Guidelines place similar emphasis on:
- Lifetsyle modifications as essential
- Importance of targeting lower LDL-C levels, using risk factors & enhancers to guide shared decision making with patients
Differences in treating high-, very high-risk patients:
- ACC/AHA adheres closely to key trial evidence to guide therapy beyond statins in patients with clinical ASCVD and prior events.
- ESC/EAS goes beyond trial data, extrapolating to patients with solely imaging evidence of ASCVD.
Guideline target for “very high-risk” patients:
- ACC/AHA: 70 mg/dL
- ESC/EAS: 55 mg/dL
Sources
Mach F, Baigent C, Catapano AL, et al. 2019 ESC/EAS Guidelines for the management of dyslipidaemias: lipid modification to reduce cardiovascular risk: The Task Force for the management of dyslipidaemias of the European Society of Cardiology (ESC) and European Atherosclerosis Society (EAS), Eur Heart J. 2019;00:1-78.
Grundy SM, Stone NJ, Bailey AL, et al. 2018 AHA/ACC/AACVPR/AAPA/ABC/ACPM/ADA/AGS/APhA/ASPC/NLA/PCNA Guideline on the Management of Blood Cholesterol: A Report of the American College of Cardiology/American Heart Association Task Force on Clinical Practice Guidelines. J Am Coll Cardiol 2018.