© 2025 MJH Life Sciences™ , Patient Care Online – Primary Care News and Clinical Resources. All rights reserved.
Novel Markers, Glycemic Variability Predict CV Events in Diabetes
From ADA 2018: Two new biomarkers predict CV events independently of conventional risk factors, plus post-hoc analysis of VADT.

Studies at the ADA 78th Scientific Sessions included evaluations of novel markers of risk for cardiovascular events, and an analysis of the relation between glycemic variation and cardiovascular risk in the Veteran Affairs Diabetes Trial (VADT).
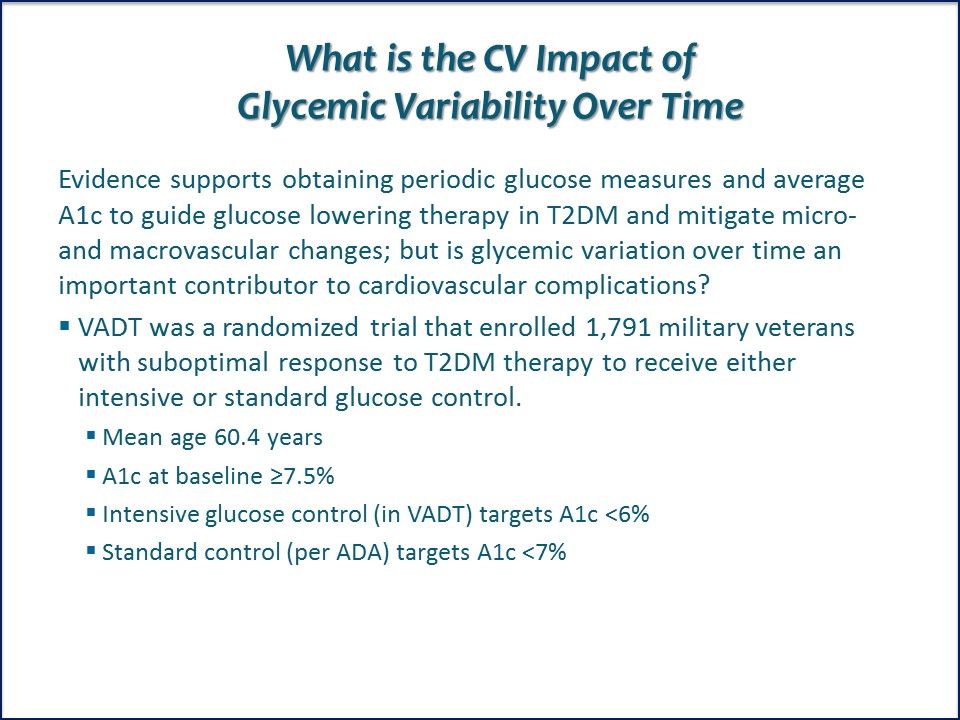
What is the CV Impact of Glycemic Variability Over Time? Should fluctuation in glycemic control over time be considered a risk factor for the development of CV complications in patients with T2DM? Does standard vs intensive glucose control make a difference?
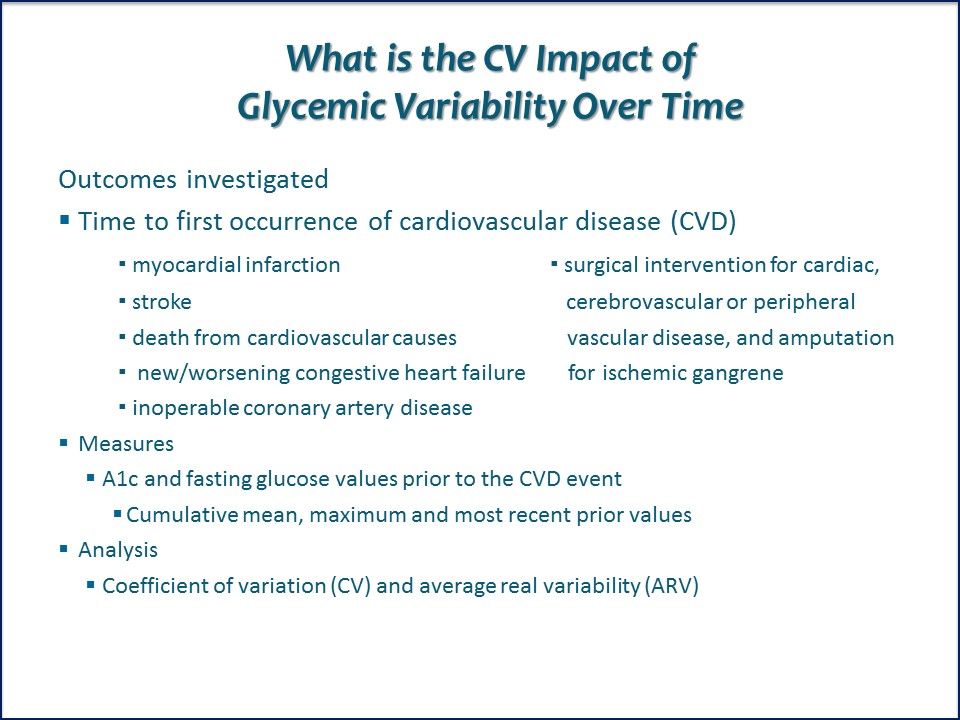
Outcomes Investigated: Time to First Occurence of CVD. Measures used, A1c and fasting glucose values prior to the CVD event; cumulative mean, maximum and most recent prior values.

Variability of Fasting Glucose Significantly Associated with CVD. Variability of fasting glucose appeared to play a role in development of CVD complications beyond the influence of standard fasting glucose measures. The adverse consequences appeared greatest in those on intensive glucose control. Link to ADA abstract.

The novel adipokine C1QTNF1 significantly predicts the incidence of future major cardiovascular events in patients with type 2 diabetes
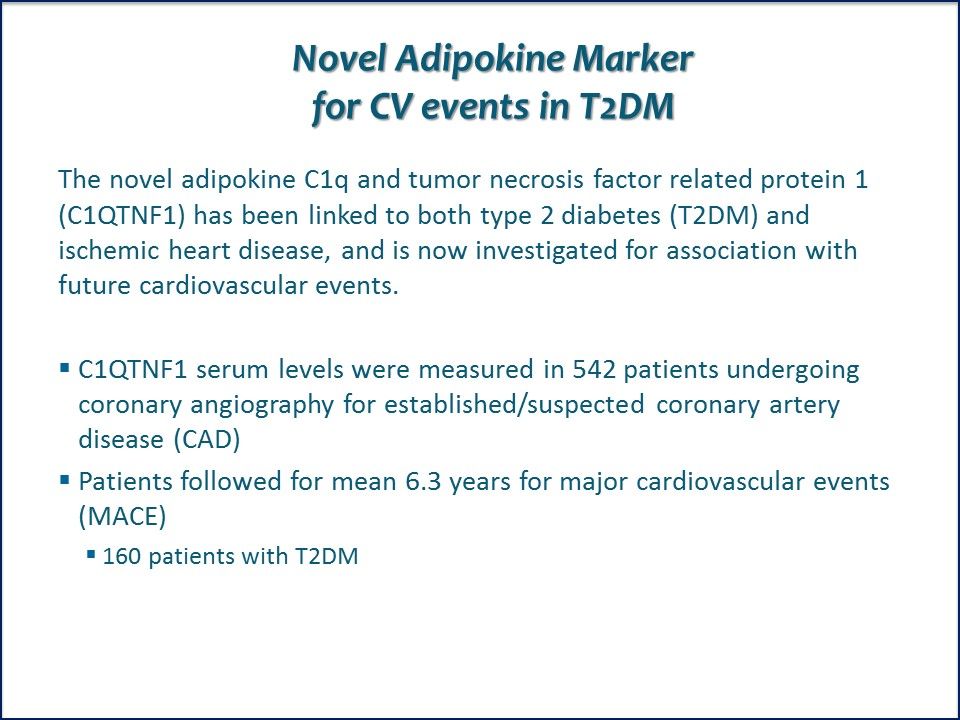
Novel Adipokine Marker for CV events in T2DM. The novel adipokine C1q and tumor necrosis factor related protein 1 (C1QTNF1) has been linked to both type 2 diabetes (T2DM) and ischemic heart disease, and is now investigated for association with future cardiovascular events.
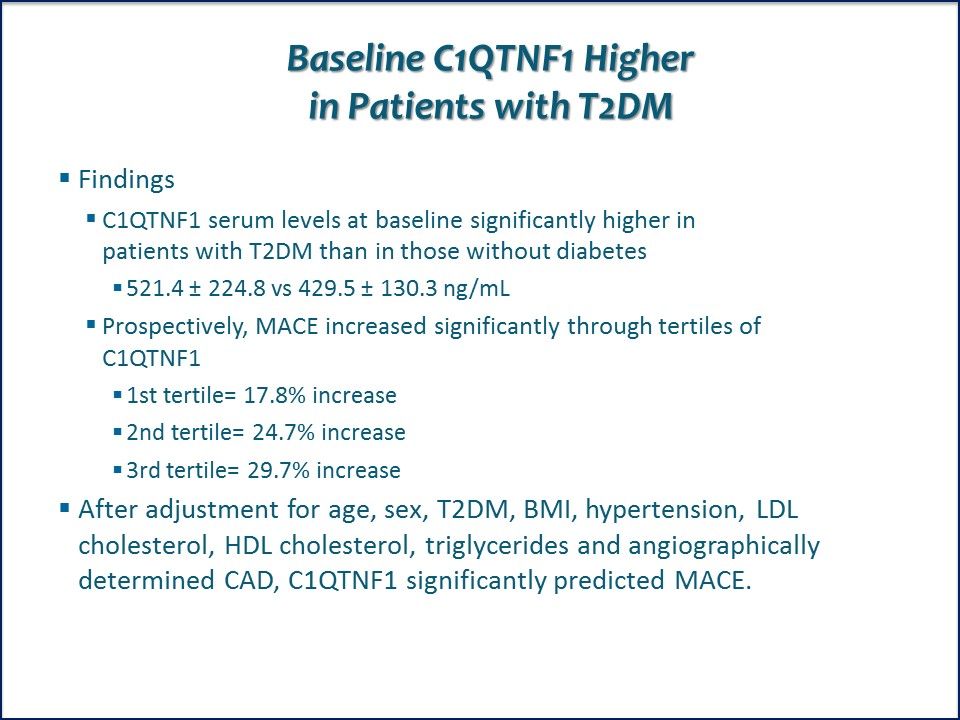
Baseline C1QTNF1 Higher in Patients with T2DM. C1QTNF1 significantly predicted MACE after adjustment for age, sex, T2DM, BMI, hypertension, LDL cholesterol, HDL cholesterol, triglycerides and angiographically determined CAD.
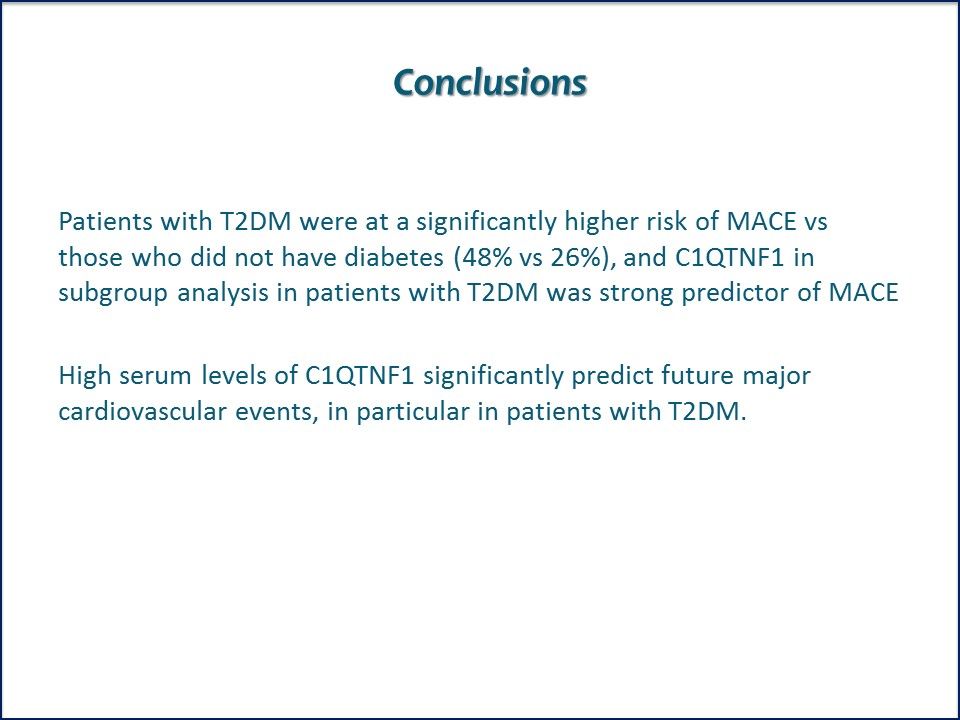
Conclusions. High serum levels of C1QTNF1 significantly predict future major cardiovascular events, in particular in patients with T2DM. Link to ADA abstract.

Betatrophin predicts cardiovascular events independently from the presence of type 2 diabetes and coronary artery disease
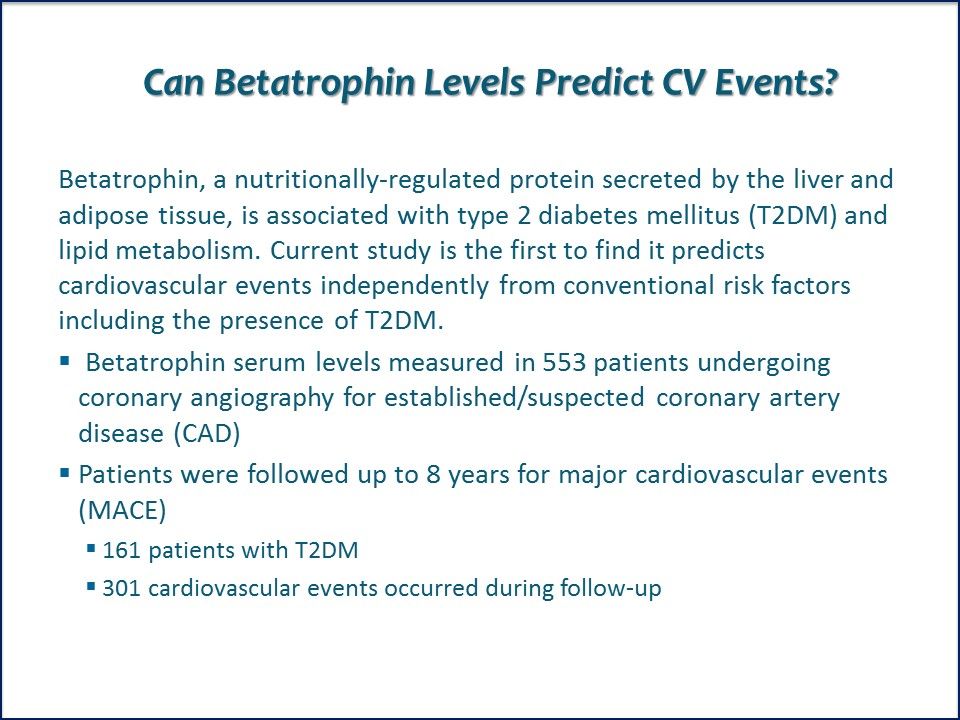
Can Betatrophin Levels Predict CV Events? Betatrophin, a nutritionally-regulated protein secreted by the liver and adipose tissue, is associated with type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) and lipid metabolism. First study to evaluate its potential role in predicting CV events.
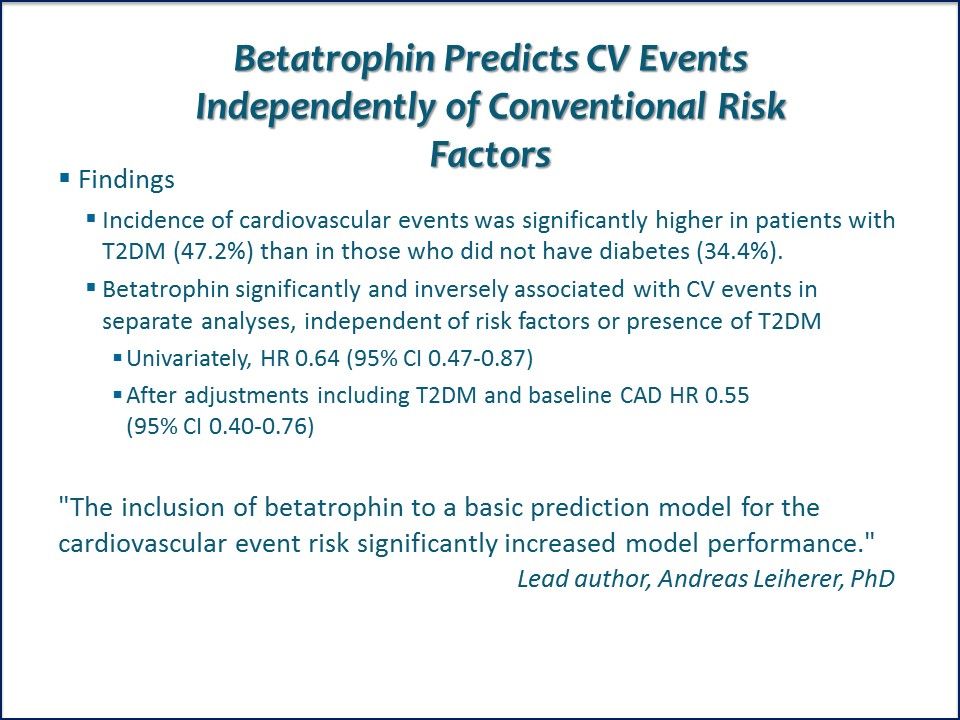
Betatrophin Predicts CV Events Independently of Conventional Risk Factors. Incidence of cardiovascular events was significantly higher in patients with T2DM (47.2%) than in those who did not have diabetes (34.4%). Authors note that "The inclusion of betatrophin to a basic prediction model for the cardiovascular event risk significantly increased model performance." Link to ADA abstract.




