© 2025 MJH Life Sciences™ , Patient Care Online – Primary Care News and Clinical Resources. All rights reserved.
Insulin Discontinuation and Other Measures of GLP-1 RA Efficacy
What is the impact on insulin dose, A1c, body weight of adding GLP-1 RA to a MDI insulin regimen? Three studies from ADA 2018 illuminate.

Three studies at ADA 78th Scientific Sessions in Orlando assessed efficacy of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor agonists (GLP-1 RA): two looked at whether insulin, both basal and prandial, could be discontinued and A1c maintained after starting the GLP-1RA and one compared 6-month and 1-year efficacy of three GLP-1 RAs as initial therapy for patients with type 2 diabetes.
Click through the slides above for higlights of all 3; links to ADA abstracts are inlcuded.

Predictive factors of insulin discontinuation after adding a GLP-1 receptor agonist in patient with type 2 diabetes treated with insulin in combination with oral antihyperglycemic agents
What Factors Predict Successful Insulin DC after Adding GLP-1 RA? Discontinuing insulin is sometimes possible after adding a GLP-1RA to an antihyperglycemic regimen in T2DM; the study sought to learn what attributues are associated wtih sustained glycemic control after stopping insulin.

Lower Insulin Dose at Baseline Strongest Predictor of Insulin DC Success. Other factors associated with success were lower fasting plasma glucose and baseline A1c; shorter duration of T2DM and of insulin therapy; and absence of diabetic renal disease.

Author's Insights. Juan Gorgojo-Martinez, MD, commented on the rationale for the study. "In some clinical trials and real-word studies, 20% - 30% of patients are able to discontinue their insulin therapy 6-12 months after initiating a GLP-1RA. However, the percentage of those patients maintaining good glycemic control without insulin remains unknown." Link to ADA abstract.

Near-normoglycemia, with meaningful discontinuations of prandial insulin, by adding weekly albiglutide (Albi) to uncontrolled basal/bolus insulin-treated type 2 diabetes

Impact on Prandial Insulin Useof Adding a GLP-1 RA? The GLP-1RA albiglutide was added to basal/bolus insulin + antihyperglycemic regimens in patients with uncontrolled T2DM to determine if the need for insulin lispro would decrease or if patients would be able to discontinue it altogether.
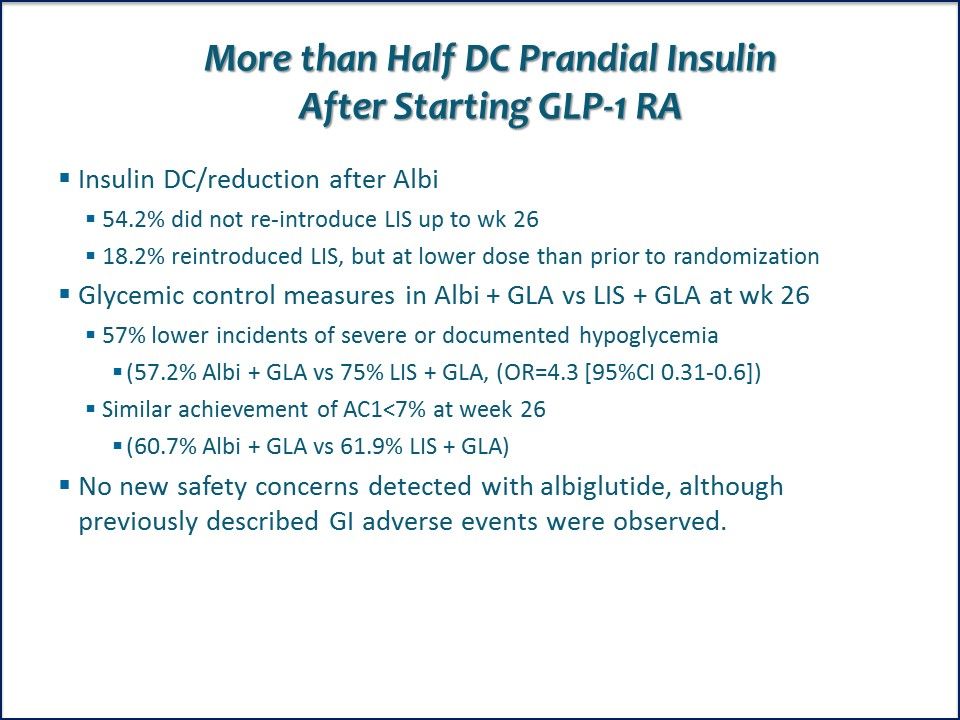
More than Half Discontinue Prandial Insulin After Starting GLP-1 RA. At week 26, 54.2% had not re-introduced insulin lispro; 18.2% had reintroduced insulin but a lower dose than before study randomization.

Author's Insights. Lead author Julio Rosenstock, MD, commented, "These findings appear to have considerable potential for improving quality of life in this group of people with advanced T2DM." Link to ADA abstract.

Comparative glycemic effectiveness of dulaglutide vs liraglutide and exenatide QW in a US real-world setting

Three GLP-1 RAs: A Close Look at Efficacy, Adherence. Mean baseline characteristics for study patients: Age: 53 years; insulin dose: 32.3 U/day; A1c: 8.78% ± 1.82. Comparisons were made between patients initiated on dulaglutide vs liraglutide and on dulaglutide vs exenatide weekly.

A1c % Lower, Adherence Better with Dulaglutide at One Year. Patients initiating dulaglutide experienced statistically significantly greater reduction in A1c than those initiated on liraglutide or exenatide weekly (p<.05). Link to ADA abstract.
Related Content:



