© 2025 MJH Life Sciences™ , Patient Care Online – Primary Care News and Clinical Resources. All rights reserved.
GI Disease in 3 Pregnant Women
Possible gastrointestinal issues during gestation range from expected to significant threat. Choose your next steps for these 3 young women.

Possible gastrointestinal issues during gestation range from expected to significant threat. Choose your next steps for these 3 young women.

Case #1. A 32-year-old woman who is 32 weeks pregnant presents with a chief complaint of daily heartburn, indigestion, and nausea. Symptoms are worse after dinner when she typically lies down on the couch, but have been somewhat improved with calcium carbonate antacids.

What is the most appropriate next step in management? Ambulatory pH testing, start ranitidine, upper endoscopy, stop calcium carbonate, lifestyle modifications
Answer: E. Lifestyle modifications. This patient has symptoms consistent with gastroesophageal reflux disease, a common condition in pregnancy. Lifestyle modification should include avoiding dietary triggers, elevating the head of bed at night, and avoiding lying recumbent right after eating.
Case #2. A 26-year-old woman with a history of Crohn disease is entering her third trimester of pregnancy. History includes ileocolonic disease and resection. She has improved significantly with infliximab therapy, but has questions about the safest delivery method for her baby.
Which of the following clinical scenarios requires cesarean section for delivery? Active perianal Crohn disease, use of anti-TNF therapy, pyoderma gangrenosum, ileal pouch-anal anastomosis, enterocutaneous fistula
Answer: A. Active perianal Crohn disease. Vaginal delivery carries a risk of perineal trauma. In patients with active perianal Crohn disease, a cesarean section is the preferred delivery method in order to avoid disease exacerbation.
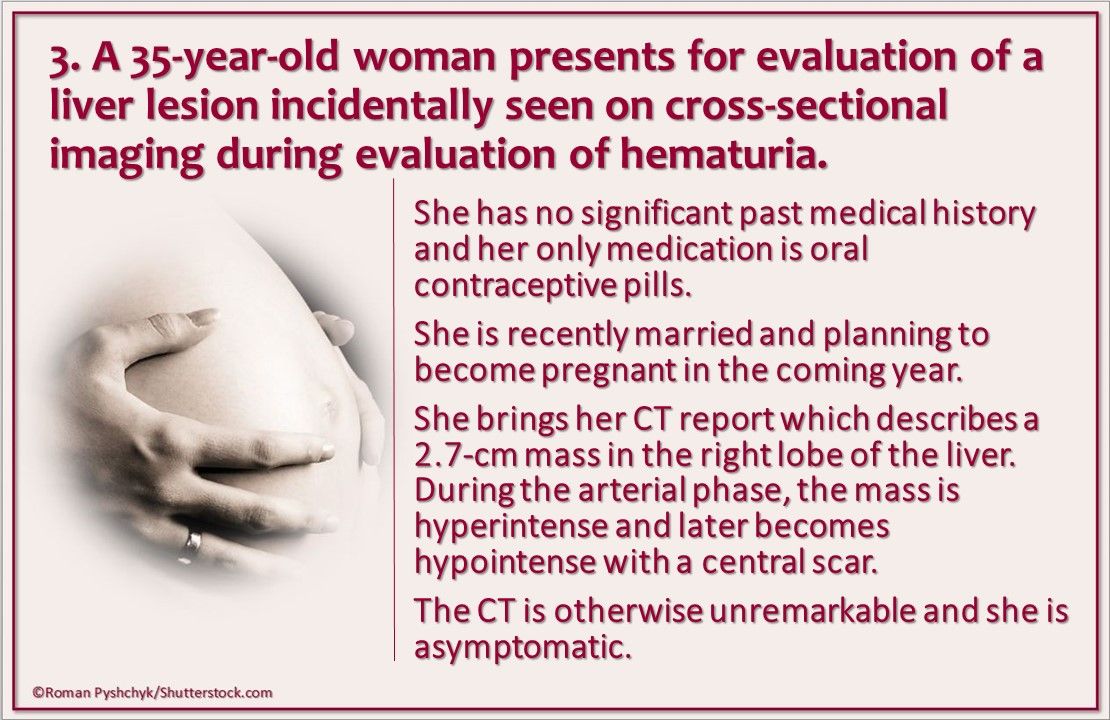
Case #3. A 35-year-old woman presents for evaluation of a liver lesionincidentally seen on cross-sectional imaging during evaluation of hematuria. The CT report describes a 2.7-cm mass in the right lobe of the liver. During the arterial phase, the mass is hyperintense and later becomes hypointense with a central scar.

What is the appropriate next step in managment? Discontinue oral contraceptive pills, reassurance alone, avoidance of pregnancy, cesarean section at time of delivery, resection of liver mass
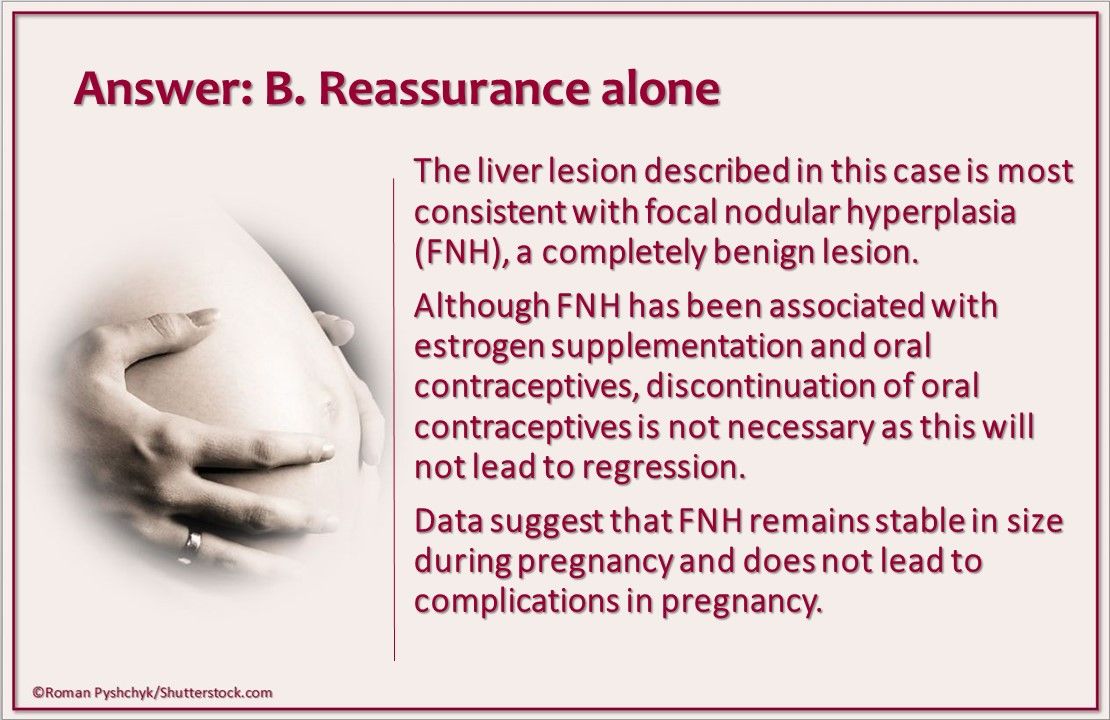
Answer: B. Reassurance alone. The description is most consistent with focal nodular hyperplasia (FNH), a benign lesion. The condition has been associated with estrogen replacement and oral contraception, but discontinuation of the latter will not lead to regression. Data suggest that FNH remains stable in size during pregnancy and does not lead to complications in pregnancy.
Follow Dr James on Twitter: @TedWJamesMD



