© 2025 MJH Life Sciences™ , Patient Care Online – Primary Care News and Clinical Resources. All rights reserved.
Getting Down to the Bare Bones: A Photo Quiz
Bone problems run the gamut from low bone density and osteoporosis to sports and exercise injuries to congenital disorders. Take this week’s photo quiz to test your knowledge of bone disease and related concerns.
Question 1:
A 21-year-old man presented for evaluation after he sprained his right ankle while hiking. Radiographs showed no fractures but revealed diffuse sclerotic lesions in most of the visualized bones.
NEXT QUESTION »
For the discussion, click here.
Question 2:
A 57-day-old girl had a scaly rash on her face and scalp; the diagnosis was seborrheic dermatitis. Later the diagnosis was amended to atopic dermatitis and, with fever and rash, to viral exanthema. At 13 months, a whitish coating developed on her tongue and lips; the diagnosis was thrush. At 19 months, with worsening rash, the diagnosis was dermatosis and edema. Then a punch biopsy showed dermal fibroplasia, dermal melanophages, and interface dermatitis. Bone marrow failure is the primary cause of death.
NEXT QUESTION »
For the discussion, click here.
Question 3:
A 69-year-old woman presented with a 5-year history of bilateral knee pain with symptoms initially attributed to osteoarthritis and then to rheumatoid arthritis. She had a history of asymptomatic Paget disease of bone. Physical examination revealed tenderness, swelling, and crepitation in both knees. X-ray films of the patient’s hands showed chondrocalcinosis of the triangular fibrocartilage, and chondrocalcinosis was seen on pelvic and knee films.
Paget disease of bone was thought to play a role in the development of her disorder.
NEXT QUESTION »
For the discussion, click here.
For the answer, click here.
Question 4:
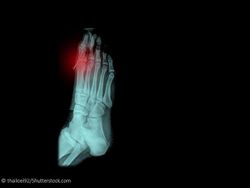
A 29-year-old man, an avid runner, presented with a 2½-year history of left midfoot pain on the dorsal area of the first metatarsal-cuneiform joint. The main area of pain appeared to be over the medial dorsal area of the forefoot, around the base of the first metatarsal bone. There was some radiating pain over the first metatarsophalangeal joint but no bruising, swelling, discoloration, skin lesion, temperature change, or obvious deformity.
NEXT QUESTION »
For the discussion, click here.
Question 5:
In this knee with advanced osteoarthritis, the joint has been opened anteriorly and the patella has been reflected downward. Large ulcerated areas of articular cartilage are present in the intercondylar region, on the femoral condyles, and on the patella. Some of the cartilage defects extend down to the subchondral bone.
NEXT QUESTION »
For the discussion, click here.
Question 6:
An axial T2-weighted, fat-saturated image shows bone marrow edema in a bone bruise. Bone marrow edema is characterized by ill-defined medullary infiltration without bone lysis. It appears hypointense on T1-weighted images and hyperintense on T2-weighted/fat-saturated or STIR images and enhanced after injection of gadolinium contrast.
NEXT QUESTION »
For the discussion, click here.
Question 7:
A 10-year-old boy had pain and swelling of the left ankle with no history of trauma, pain in other joints, fever, fatigue, or decreased appetite. Point tenderness was marked over the medial malleolus and over the shaft of the fifth metatarsal distally. Radiographs revealed a 13-mm lytic lesion in the left distal tibia and an 8-mm lytic lesion in the left fifth metatarsal. There were no other bone lesions. He underwent bone biopsy with aspiration of both lesions. The diagnosis was revealed by histological examination of the aspirate.
ANSWER KEY »
For the discussion, click here.
ANSWER KEY:
Question 1. C
Question 2. B
Question 3. C
Question 4. A
Question 5. C
Question 6. B
Question 7. B