© 2025 MJH Life Sciences™ , Patient Care Online – Primary Care News and Clinical Resources. All rights reserved.
Asthma Research Update: 7 Studies At-a-Glance for Primary Care
Recent studies have reported the latest developments in asthma research. Scroll through these slides to find concise summaries of key points for clinical practice.
Recent studies have reported the latest developments in asthma research. Scroll through the slides below to find concise summaries of key points for clinical practice.

Concurrency and comorbidity. A comorbidity profile emerges from a recent study of diagnoses of statutory health insurees in Germany. Of the 11% who had a diagnosis of asthma or COPD, 43% had asthma only, 44% COPD only, and 13% both. Concurrent asthma/COPD prevalence was 1.5%. Common comorbid disorders included other respiratory diseases, bacterial infections, and fungal infections. The authors recommended a multidisciplinary care approach and regular screening for comorbidities. Scientific Reports.

Greater mortality in young. Asthma is associated with increased mortality in children and young adults regardless of whether they have an LLC or of their parents’ SES, a study found. For all-cause mortality in asthma vs non-asthma cases, the adjusted hazard rate was 1.46. In those who had asthma but not an LLC, it was increased at 1.33; in those with asthma and an LLC, it was 1.87. Parental SES (income, education) did not alter the association. Thorax.

Allergic multimorbidity means more symptoms. Patients who had asthma and allergic multimorbidity—rhinitis and eczema—were more likely to be sensitized to seasonal allergens and food allergens and to have a higher degree of sensitization than those who had only asthma. They had more allergic reactions to food, respiratory symptoms, and anxiety/depression and were more likely to receive an asthma diagnosis before age 12 and have maternal heredity for allergy. Clinical & Experimental Allergy.
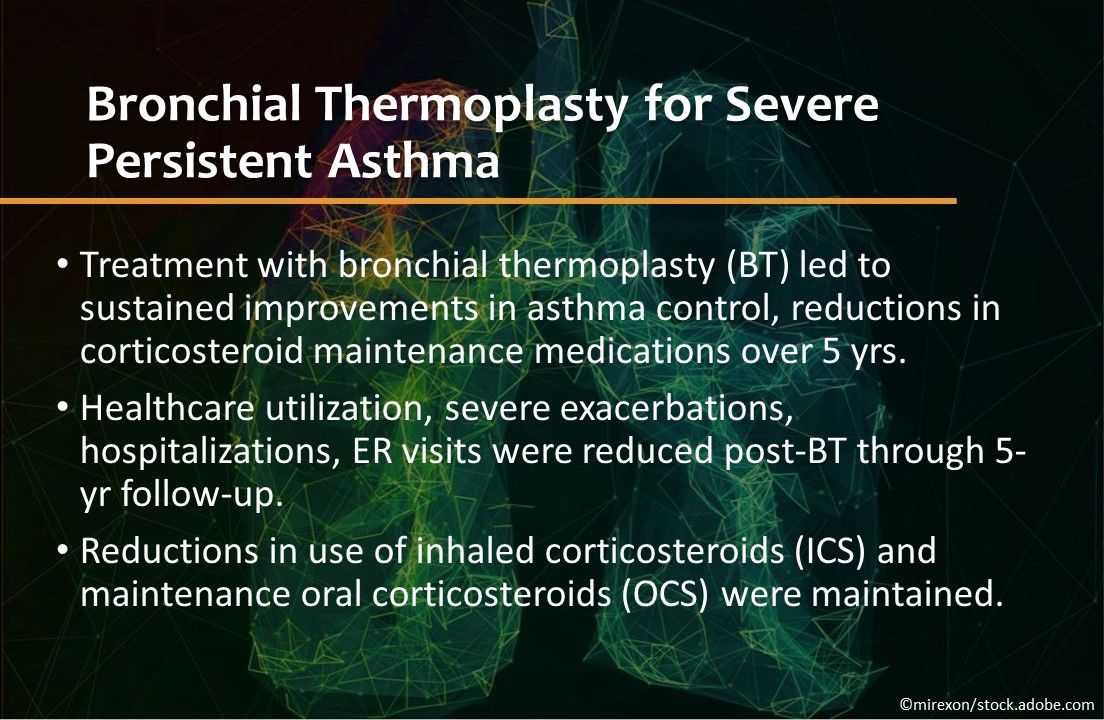
Bronchial thermoplasty for severe persistent asthma. Treatment with BT led to sustained improvements in asthma control and reductions in corticosteroid maintenance medications over 5 years in a prospective study. Health care utilization, severe exacerbations, hospitalizations, and ER visits were reduced post-BT through 5-year follow-up, and reductions in use of ICS and maintenance OCS were maintained. CHEST Virtual Annual Meeting.
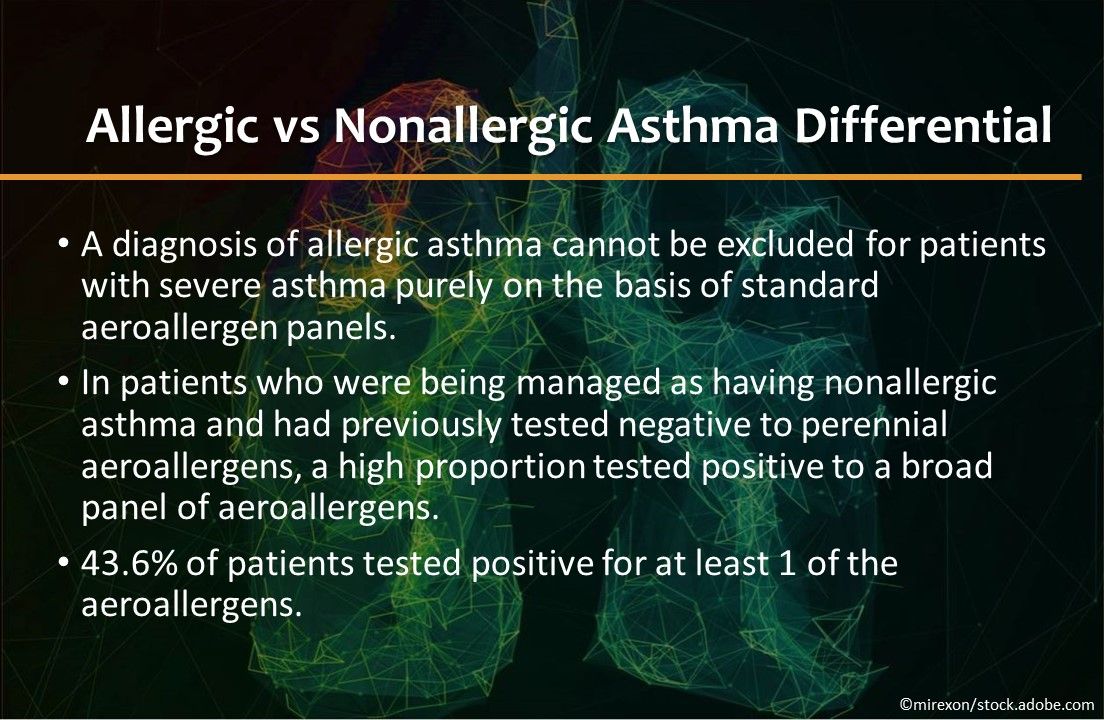
Allergic vs nonallergic asthma differential. For patients with severe asthma, a diagnosis of allergic asthma cannot be excluded purely on the basis of standard aeroallergen panels, researchers found. In patients who were being managed as having nonallergic asthma and had previously tested negative to perennial aeroallergens, a high proportion tested positive to a broad panel of aeroallergens; 43.6% of patients tested positive for at least 1 of the aeroallergens. Allergy, Asthma & Clinical Immunology.

Corticosteroids place bone health at risk. Exposure to OCS or ICS is an independent risk factor for bone health in patients who have asthma. Nested case-control studies showed a dose-response relationship between both cumulative dose and number of prescriptions within the previous year and osteoporosis or fragility fracture risk. Patients who received more OCS prescriptions (≥9 vs 0) had a 4.50 and 2.16 increased risk of osteoporosis and fragility fracture, respectively. For ICS (≥11 vs 0), the odds ratios were 1.60 and 1.31. The cumulative dose had a similar effect. Thorax.

Parental distress in pregnancy raises asthma risk in children. Maternal psychological distress during pregnancy is associated with an increased risk of asthma and partly lower lung function in children. In a recent study of 4231 children, all maternal psychological distress measures during pregnancy were associated with an increased risk of asthma. The results were independent of maternal psychological distress after pregnancy and paternal psychological distress during and after pregnancy. Thorax.




