© 2025 MJH Life Sciences™ , Patient Care Online – Primary Care News and Clinical Resources. All rights reserved.
ADA 2018: CV Benefits of SGLT-2 Inhibitors
Three studies at ADA 2018 highlight the current track record of SGLT-2is in reducing CV-related morbidity and mortality.

A number of studies at the ADA 78th Scientific Sessions examined the cardiovascular (CV) benefits of the newer classes of antihyperglycemics--SGLT-2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists. Click through the slides above for highlights of three of them:
- The impact of empagliflozin on mortality and hospitalization for heart failure
- A comparison of CV outcomes with dapagliflozin vs the DPP-4 inhibitor class
- Comparative CV efficacy of SGLT-2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, and GLP-1 receptor agonists

Empagliflozin (EMPA) reduces mortality and hospitalization for heart failure (HF) irrespective of cardiovascular risk score at baseline
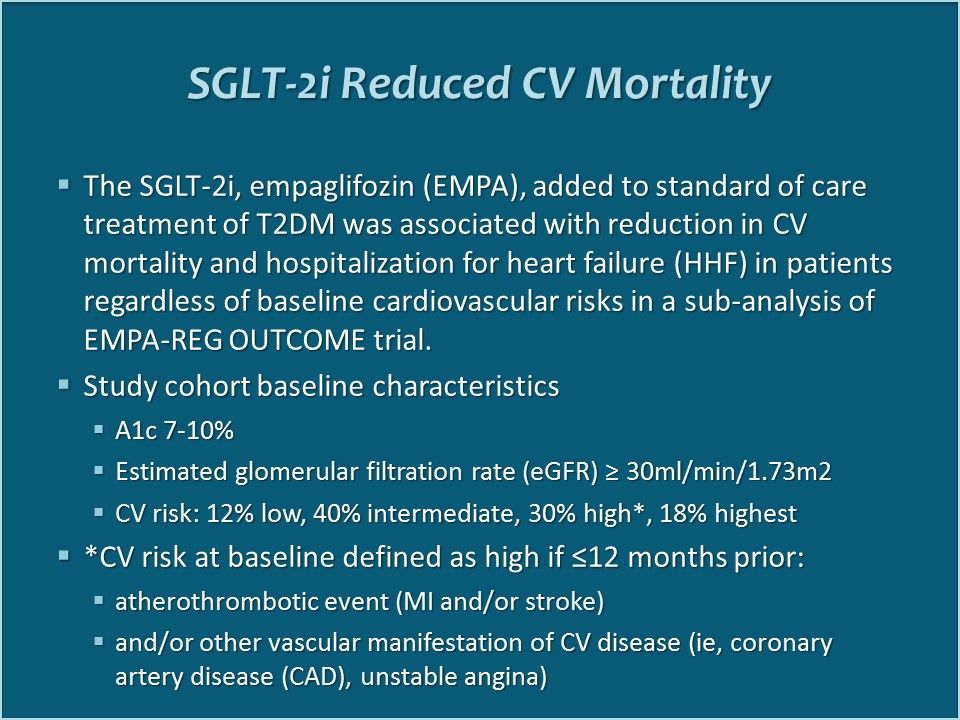
SGLT-2i Reduced CV Mortality. Study was a sub-analysis of EMPA-REG OUTCOME trial--a randomized, placebo controlled trial of adding EMPA to antihyperglycemic regimen for 7,020 patients with T2DM, designed to continue until ≥691 patients experienced adverse CV event.
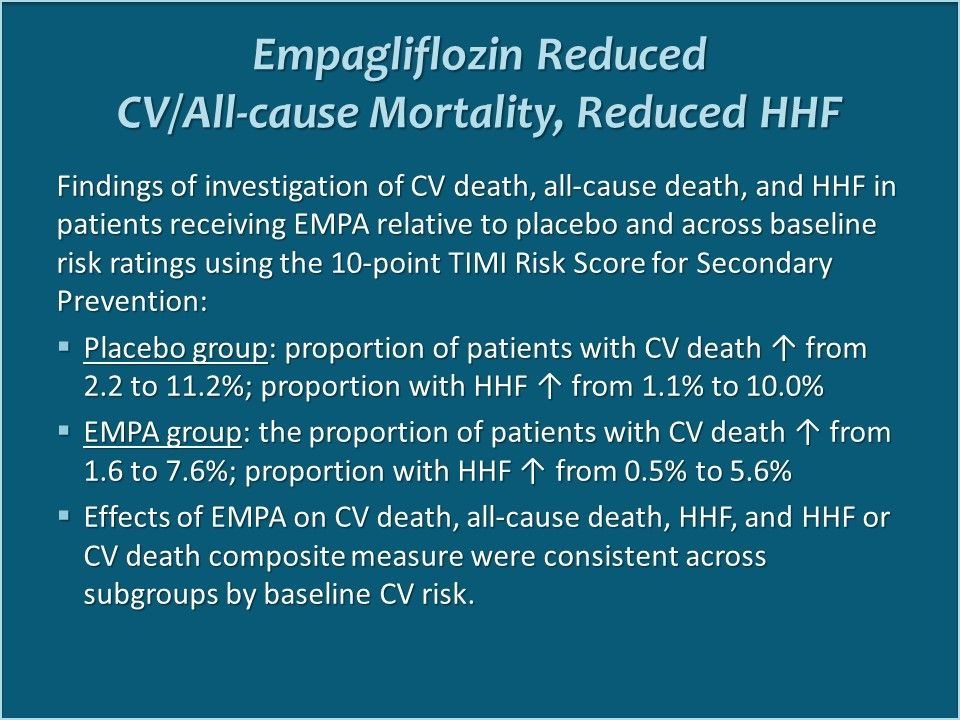
Empagliflozin Reduced CV/All-cause Mortality, Reduced HHF. Effects of EMPA on CV death, all-cause death, HHF, and HHF or CV death composite measure were consistent across subgroups by baseline CV risk.

Author's Comment. Lead study author David Fitchett, MD, noted that "Empagliflozin has a robust treatment effect in reducing mortality and HHF across a spectrum of CV risk. These findings suggest that treatment with empagliflozin could benefit patients across T2DM and CV disease irrespective of the CV risk burden." Link to ADA abstract.

Lower risk of CV events and death associated with the initiation of SGLT-2 vs DPP-4 inhibitors: Analysis from the CVD-REAL 2 Study
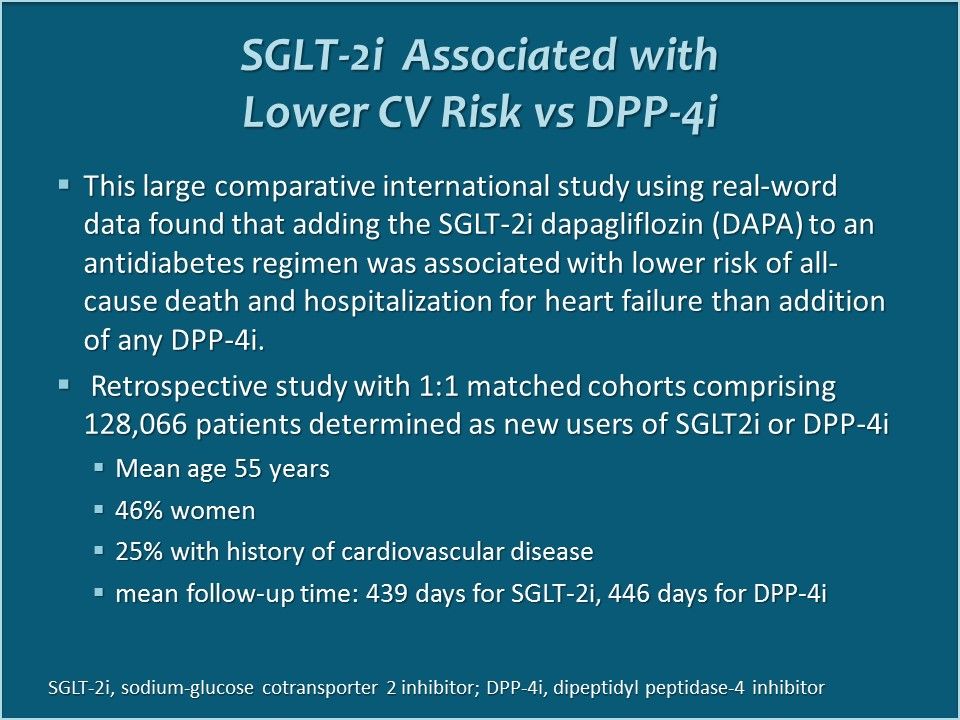
SGLT-2i Associated with Lower CV Risk vs DPP-4i. This large comparative international study using real-word data looked at the impact on all-cause death and HHF of adding dapagliflozin to an antidiabetes regimen vs adding any DPP-4 inhibitor.

CV Outcomes Parallel All-cause Deaths. Hazard ratios for all-cause death consistently favored SGLT-2i vs DPP-4i in all countries. Directionally same results in other cardiovascular outcomes including HHF favor SGLT-2i but only modestly so for MI and stroke.

Author's Comment. "These findings are complimentary to previous observed study results and clinical trials which did not include head-to-head comparisons of SGLT-2i with specific glucose-lowering drug classes," observed lead study author Shun Kohsaka, MD. Link to ADA abstract.

Comparative cardiovascular efficacy of SGLT2 inhibitors, DPP-4 inhibitors, and GLP-1 agonists: A network meta-analysis

SGLT-2i, DPP-4i, GLP-1 RAs Ranked for CV Efficacy. Meta-analysis of 236 RCTs in patients with T2DM ranked for efficacy in reducing CV-related morbidity/mortality. RCTs of >12 wks in which a SGLT-2i, DP4-i or GLP-1RA was compared with another included class or control.

SGLT-2i, GLP-1 RA Show Greatest CV Benefits. Empagliflozin (SGLT-2i) and liraglutide (GLP-1RA), demonstrate the greatest efficacy for cardiovascular mortality, while SGLT-2i may exert additional benefits in heart failure.

Author's Comment. Lead author Alistair Roddick noted, “This study provides evidence to support clinical decisions in treatment of type 2 diabetes.” Link to ADA abstract.
Related Content:



