© 2025 MJH Life Sciences™ , Patient Care Online – Primary Care News and Clinical Resources. All rights reserved.
Acute Low Back Pain: 10 Questions on Risk Factors, Diagnosis
Acute low back pain remains one of the most common reasons for a healthcare visit. Try these 10 questions on a new analysis of risk factors and diagnosis.
A recent paper published in the journal Pain Medicine presents results of a multidisciplinary review of risk factors related to the etiology and diagnosis of acute low back pain (LBP).
Following are 10 questions based on the findings. Some of the answers may be familiar to primary care practitioners; others might be surprising.
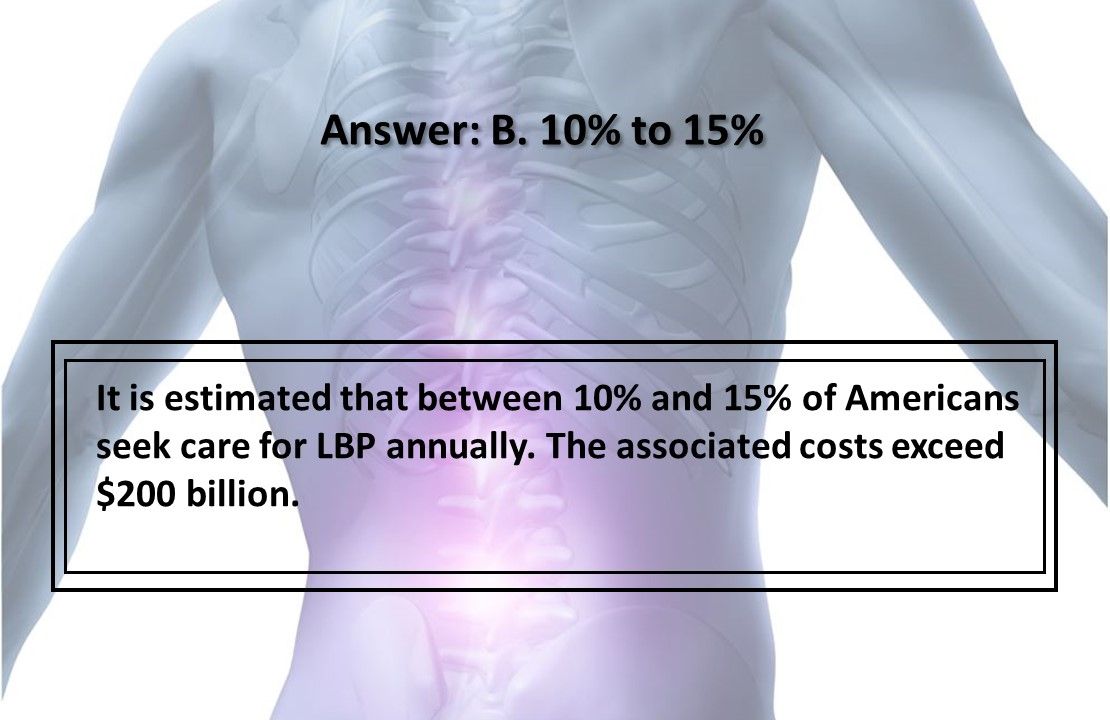
Answer B. 10% to 15%.
It is estimated that between 10% and 15% of Americans seek care for LBP annually. The associated costs exceed $200 billion.

2. True or False? The majority of people who suffer an episode of acute LBP will experience future episodes.
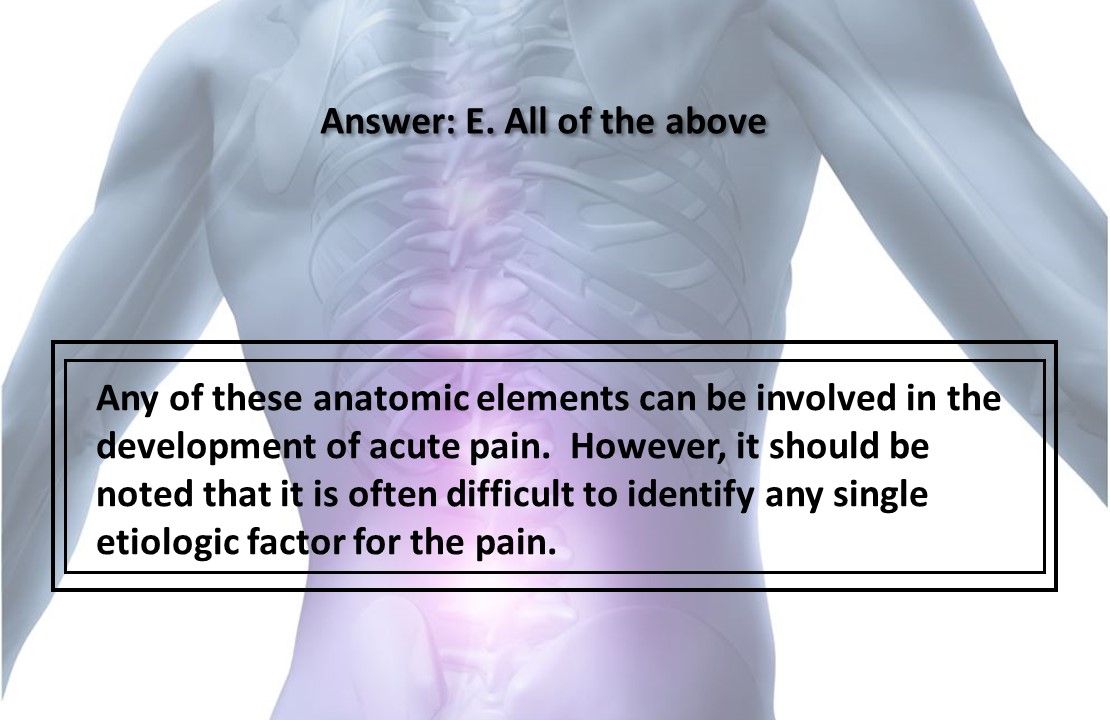
Answer: E. All the above
Any of these anatomic elements can be involved in the development of acute pain. However, it should be noted that it is often difficult to identify any single etiologic factor for the pain.
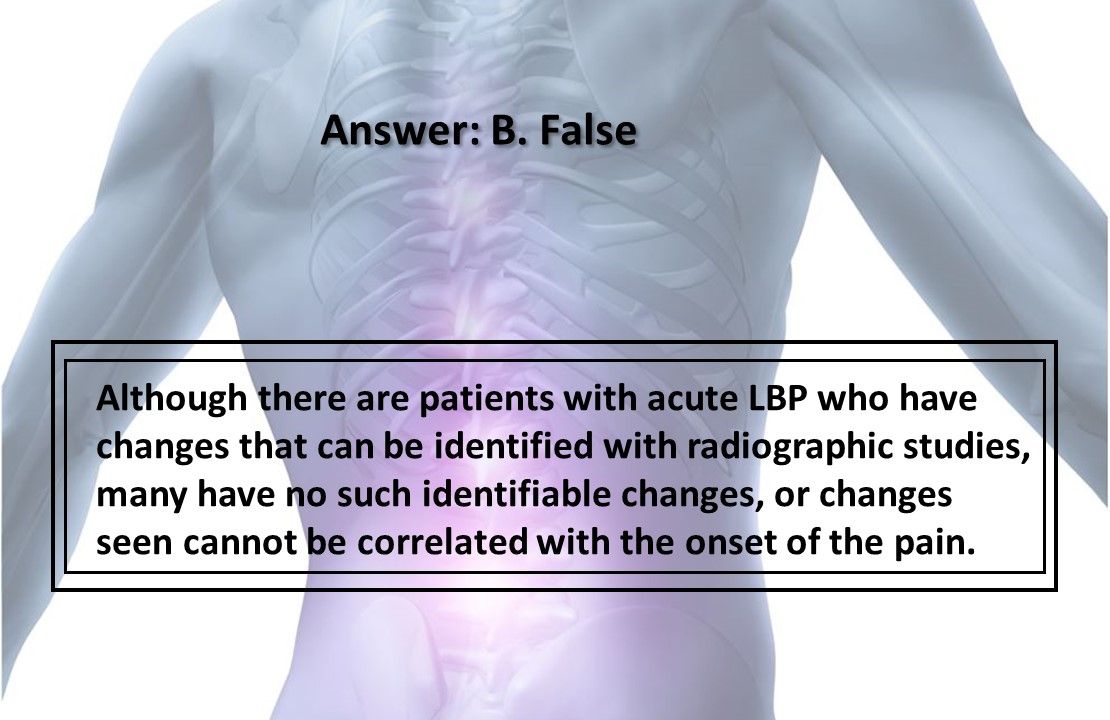
Answer: B. False
Although there are patients with acute LBP who have changes that can be identified with radiographic studies, many have no such identifiable changes, or changes seen cannot be correlated with the onset of the pain.
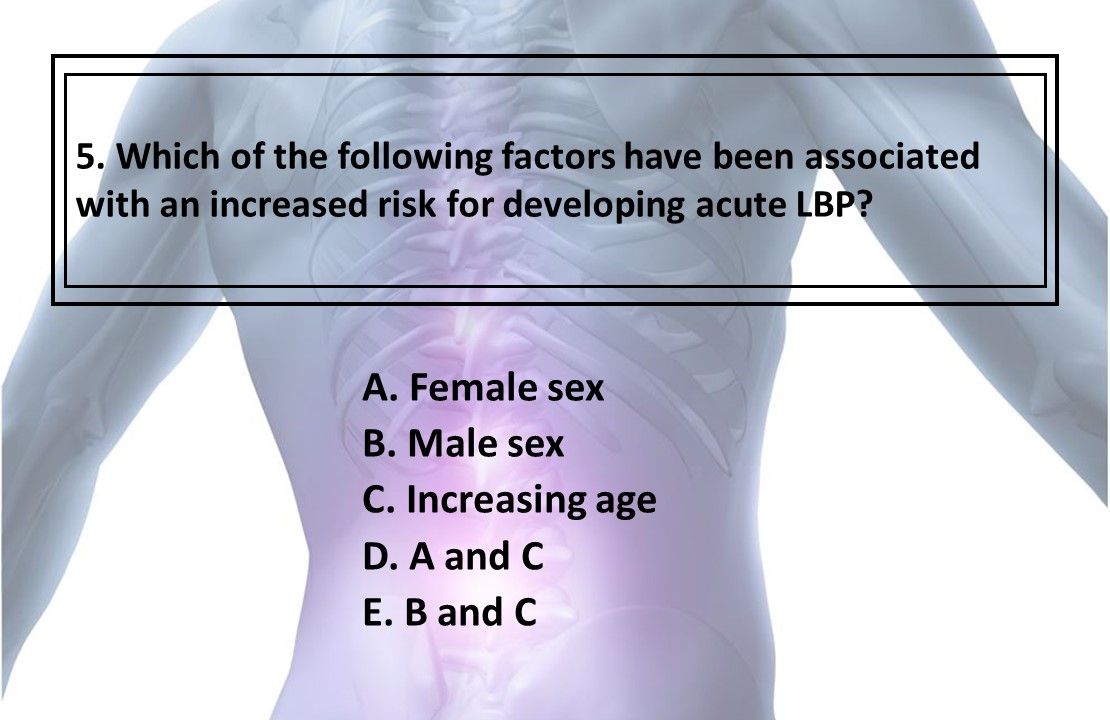
5. Which of the factors above has/have been associated with an increased risk for developing acute LBP?
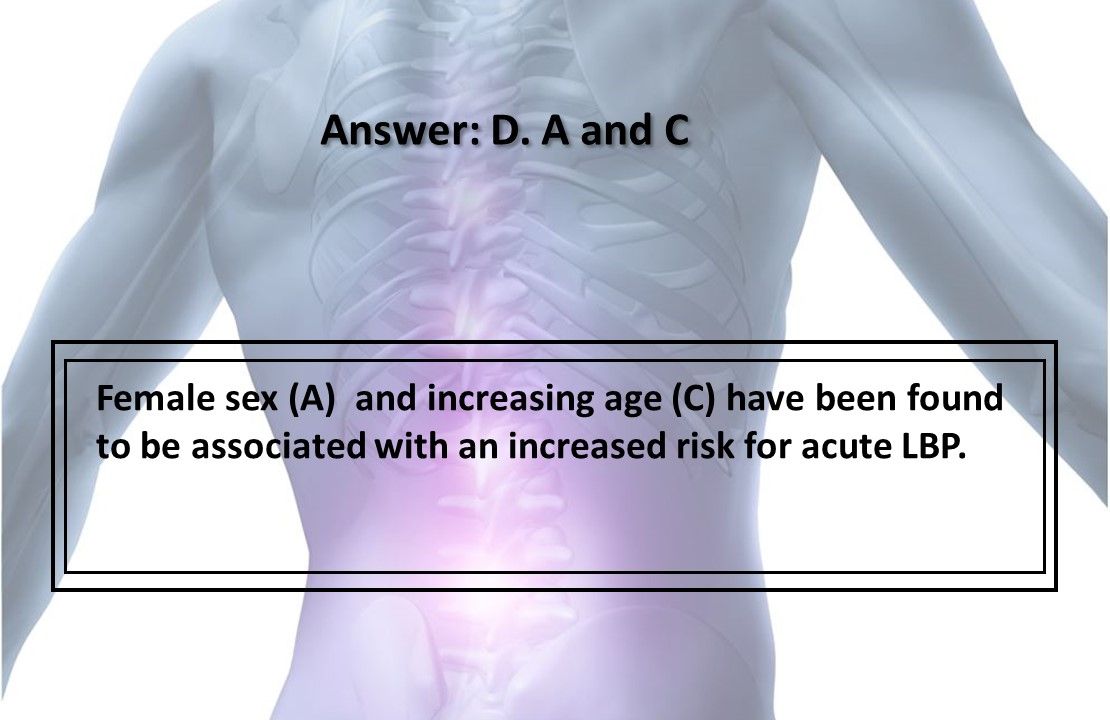
Answer: D. A and C
Female sex (A) and increasing age (C) have been found to be associated with an increased risk for acute LBP.

6. Which of the following occupational factors above is/are associated with increased risk for developing acute LBP?

Answer: D. A and C
Sedentary work (A) and job dissatisfaction (C) have both been associated with an increased risk for onset of acute LBP.

7. Which of the health issues above has/have been linked to an increased risk for developing acute LBP?

Answer: F. A and C
Obesity (A) and tobacco use (C) appear to increase the risk for development of LBP. There is little evidence indicating that either alcohol use or chronic use of opioid analgesics is associated with greater risk.

8. True or False? Increased psychological stress has been found to be an risk factor for the development of acute LBP.

Answer: A. True
Psychological stress is associated with an increased risk for developing acute LBP. In treating patients with acute LBP, it is important to identify the presence of any stresses in their lives as failure to do so may prevent successful treatment and result in the pain becoming chronic.

Answer D. All the above
Research indicates that many factors including inflammatory response and genotype may play a role in acute LBP and particularly in whether it will become chronic.
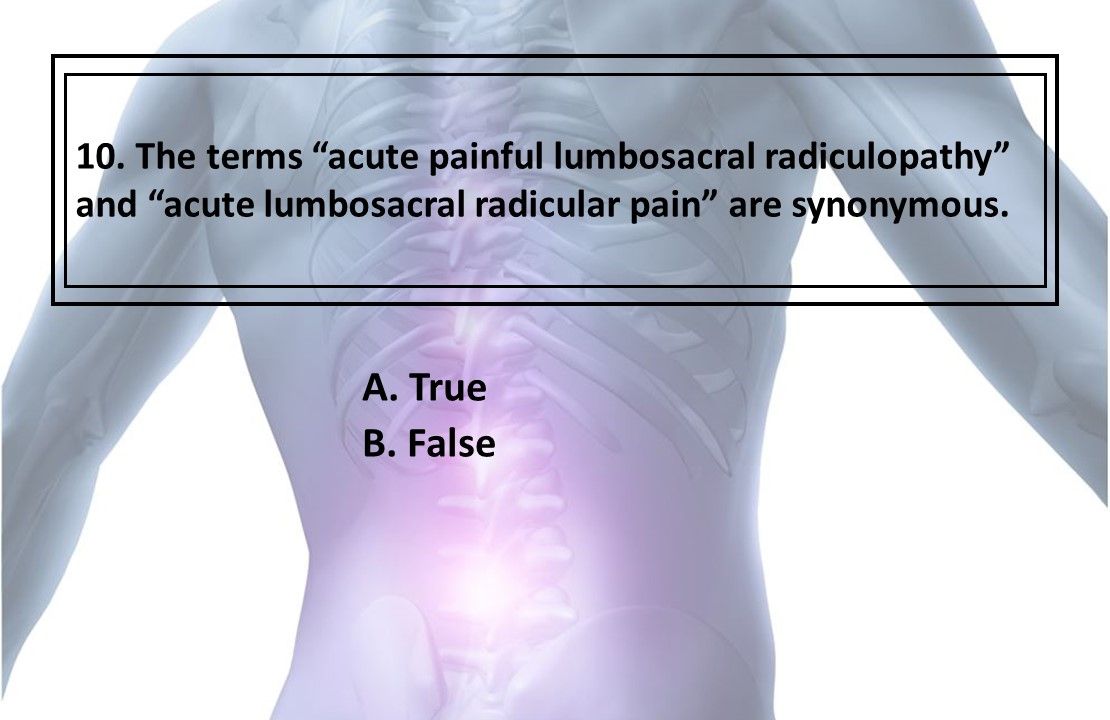
10. True or False? The terms “acute painful lumbosacral radiculopathy” and “acute lumbosacral radicular pain” are synonymous.
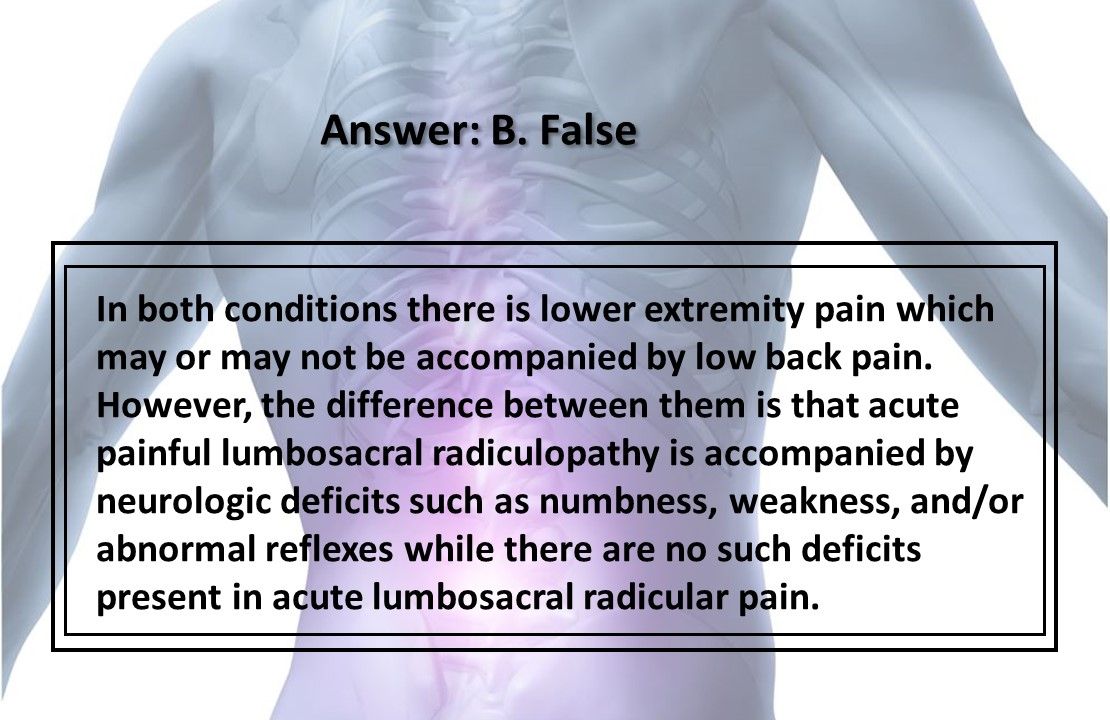
B. False
In both conditions there is lower extremity pain which may or may not be accompanied by low back pain. However, the difference between them is that acute painful lumbosacral radiculopathy is accompanied by neurologic deficits such as numbness, weakness, and/or abnormal reflexes while there are no such deficits present in acute lumbosacral radicular pain.
Related Content:









