© 2025 MJH Life Sciences™ , Patient Care Online – Primary Care News and Clinical Resources. All rights reserved.
6 Top Primary Care Items From Around the Web
A look around the web at breaking news -- not all of it medical.

Austin Frakt of The New York Times reported on an article published in the journal Alcoholism: Clinical and Experimental Research, which looked at the efficacy of Alcoholics Anonymous. Humphreys and colleagues found that for most people looking for help for alcohol problems, increasing AA attendance leads to short- and long-term decreases in alcohol consumption that cannot be attributed to self-selection.http://www.nytimes.com/2015/04/07/upshot/alcoholics-anonymous-and-the-challenge-of-evidence-based-medicine.html?mwrsm=Email&abt=0002&abg=0http://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/10.1111/acer.12557/abstractImage: ©M.UnalOzmen/Shutterstock.com

Nicholas Bakalar, of The New York Times, reported on a study published online in The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism, which found that compared with morning people, men who were night owls were significantly more likely to have diabetes, and women night owls were more than twice as likely to have metabolic syndrome.http://well.blogs.nytimes.com/2015/04/08/being-a-night-owl-may-be-bad-for-your-health/?ref=health&_r=0 http://press.endocrine.org/doi/10.1210/jc.2014-3754Image: ©Csehak Szabolcs/Shutterstock.com

Bacteria and chemicals found on human skin have been sampled and mapped across the human body. Meera Senthilingam at www.CNN.com reports on a series of eye-popping 3-D images that show the microbes and molecules people carry with them -- or on them -- each day. http://www.cnn.com/2015/04/09/health/3d-map-human-skin-bacteria-chemicals/index.htmlImage: ©vitstudio/Shutterstock.com

A moving piece by Philip Gourevitch on the Germanwings Flight 9525 tragedy over the French Alps.http://www.newyorker.com/news/daily-comment/a-bewildering-crashImage: ©Iamnong27/Shutterstock.com

Kevin Hill, MD, MS, an addiction psychiatrist, sifts through the myths about the drug and delivers a comprehensive guide.http://www.hazelden.org/mobilestore/product.html?type=item&item=314127
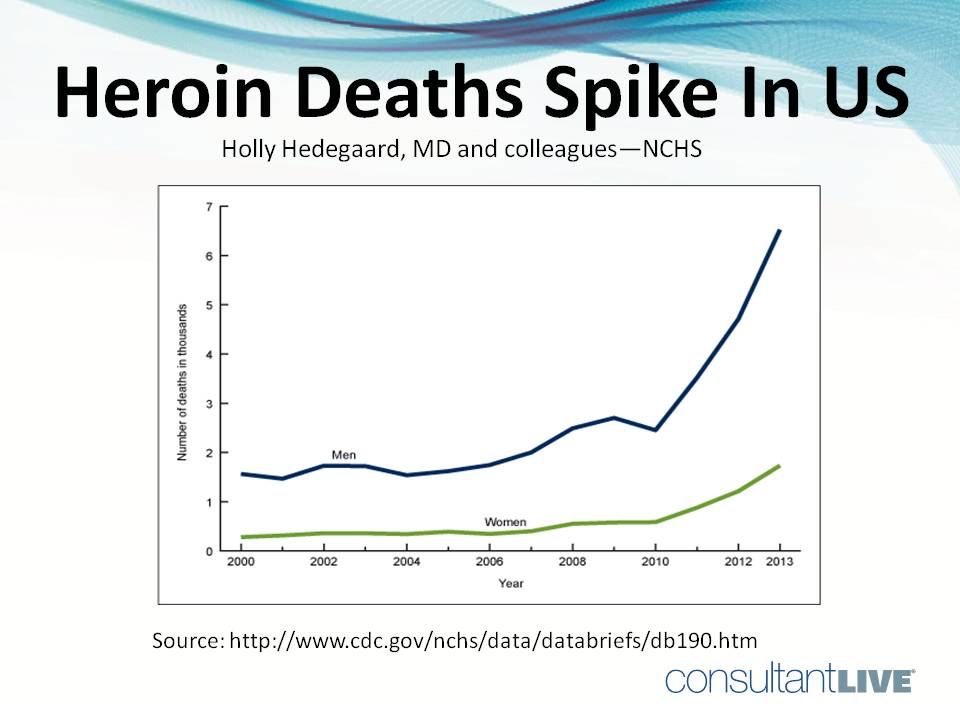
The CDC reports that from 2000 through 2013, the age-adjusted rate for drug-poisoning deaths involving heroin nearly quadrupled from 0.7 deaths per 100,000 in 2000 to 2.7 deaths per 100,000 in 2013. http://www.cdc.gov/nchs/data/databriefs/db190.htm
Here, in no particular order and randomly chosen, is a look at a collection of recent news reports, clinical articles, and books we think you'll find intriguing.

